DermaMark: A Novel Biopsy Localization Device for Dermatologic Application
- Program: Biomedical Engineering
- Course: BME Undergraduate Design Team
Project Description:
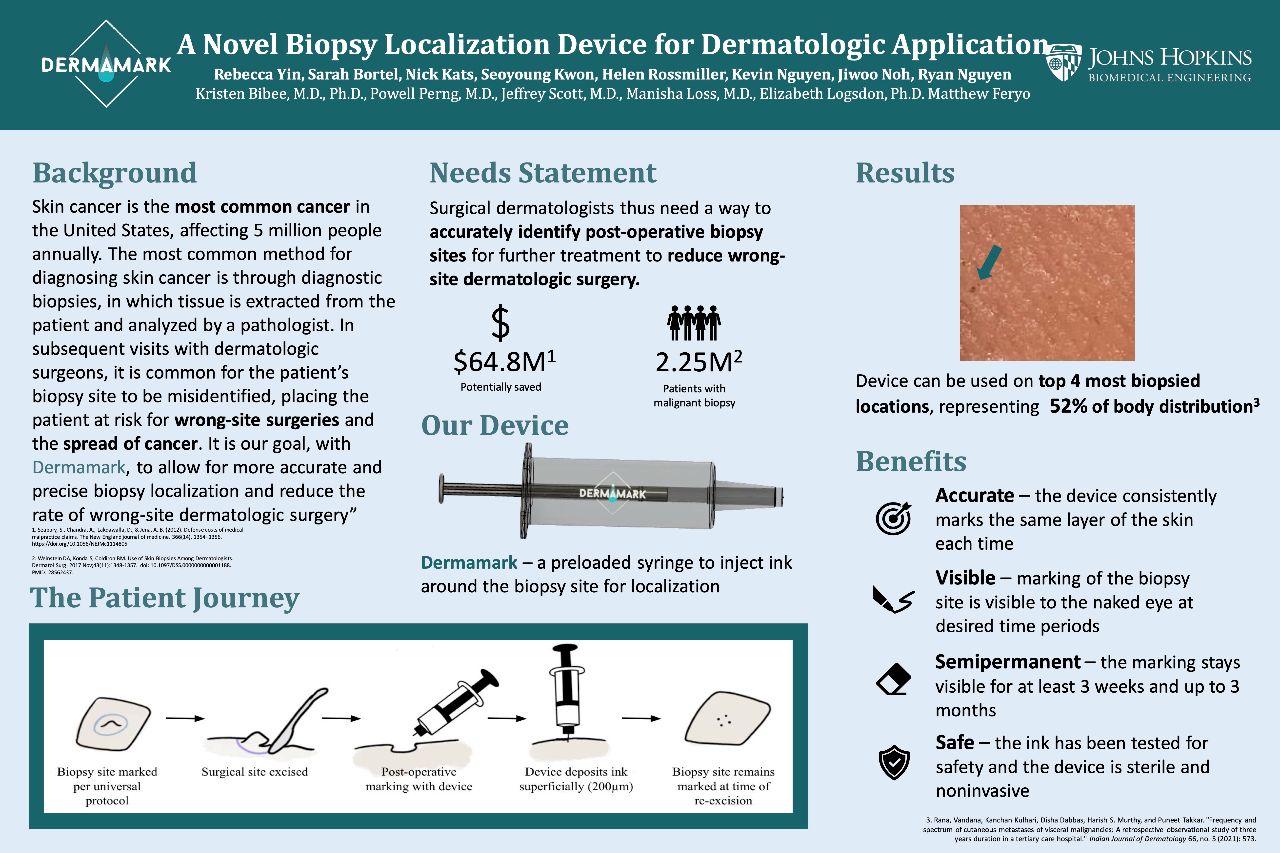
Every year, 5 million people are diagnosed with skin cancer and skin biopsies are the most common method of diagnosis. Skin biopsies are used to diagnose benign and malignant skin neoplasms. First, a dermatologist decides if a biopsy is needed based on the clinical characteristics of a lesion. If deemed worrisome, the lesion is then biopsied and sent to a pathology laboratory for evaluation. Analysis of the skin sample can take several weeks. For lesions that are malignant, a second procedure is typically recommended to remove the entire lesion. This procedure may be scheduled weeks to months after the biopsy, depending on the pathology and patient-related factors. If the patient comes in for a second procedure, the original biopsy site can be hard to identify due to surrounding lesions, previous biopsies, complete healing, actinic damage, scarring, or an area that does not have many anatomical landmarks (e.g. scalp, back). Although site misidentification is uncommon, accounting for 1.3-1.9% of all complications, it can have disastrous outcomes, including the continued development of cancer as well as financial and legal complications for both patients and healthcare providers.
Following research on available solutions, DermaMark developed a semi-permanent marking device. This device, used at the time of the biopsy, will mark the biopsy site allowing healthcare providers to identify the biopsy site up to months after the original sample is taken. Additionally, this allows patients that do not require a second procedure to have a marking that will fade after a few months.