Velocigraft: Economical Skin Meshing for Burn Surgery in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Program: Biomedical Engineering
- Course: EN.580.X12 BME Design Team
Project Description:
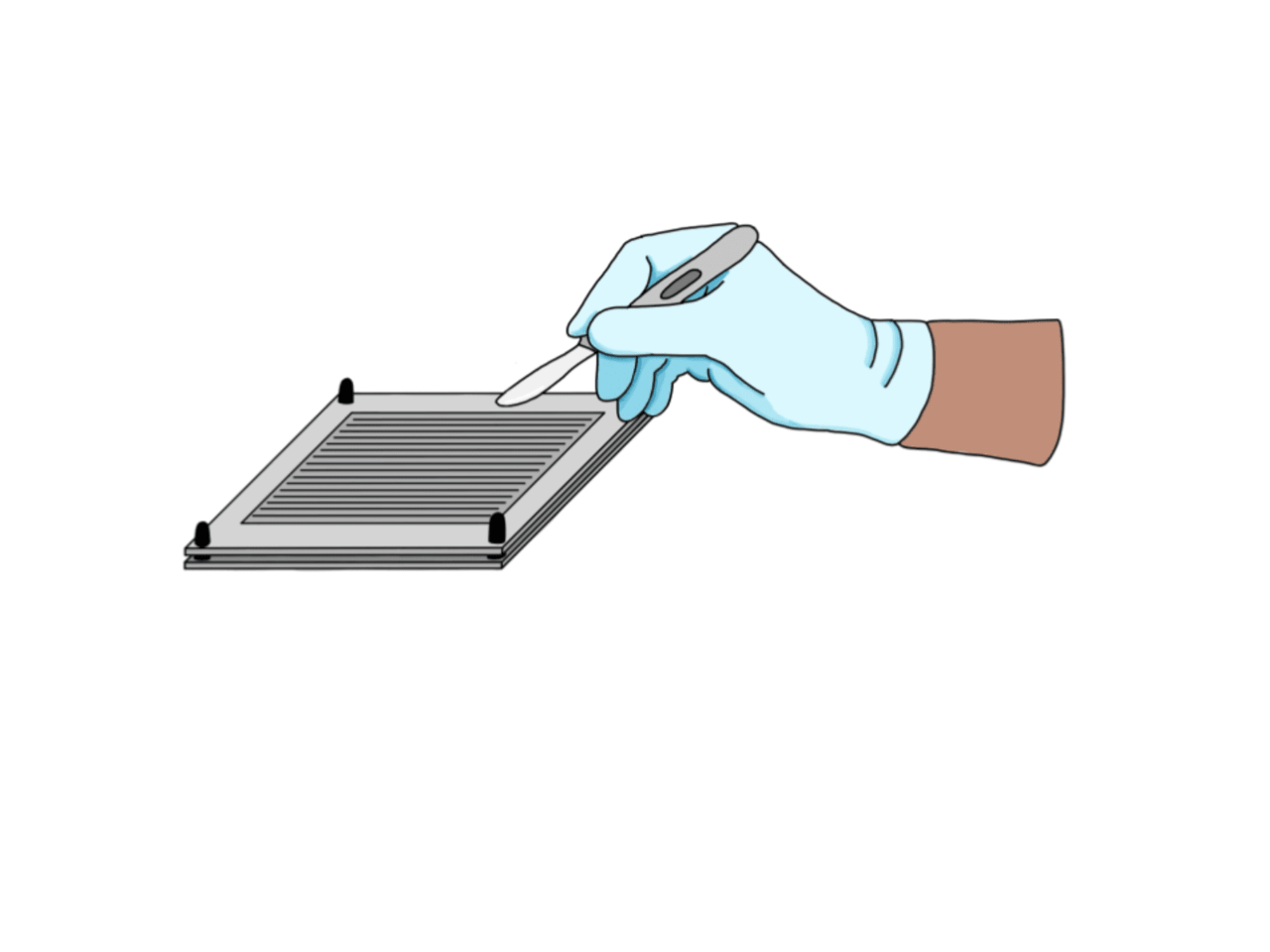
Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) accounts for 24% of the world’s 180,000 annual burn deaths despite comprising only 15% of the world’s population. Skin grafting is the gold standard for treating extensive burns, but commercial skin meshers are scarce in SSA due to high costs. Surgeons often rely on labor-intensive hand-meshing using a scalpel. The proposed solution is a low-cost, reusable template for guiding hand-meshing of autograft skin. Preliminary results on tattoo practice skin show that meshing with the template takes under a minute, compared to over 5 minutes for hand-meshing. The template can also achieve an expansion ratio of up to 1.70:1, with an average interstitial area of 1.66 cm^2. Future efforts will aim to produce a template achieving an expansion ratio of at least 2:1.
Student Team Members
- Team Leader: Ojas Chahal
- Ashley Cluff
- Dalhart Dobbs
- Aarushi Pant
- Thoya Raman
- Paree Sharma
- Aditya Shrinivasan
- Christine Wang
- Joanne Wang
- Arushi Biswas
Project Mentors, Sponsors, and Partners
- Mark Fisher, MD
- Pedro Santos, MD
- Cameron Gibson, MD
- Pallavi Ekbote