A 3D Microvessel Model of Pancreatic Cancer Revealing Tumor-Vascular Interactions and Intravasation
Team: Joanna Maressa
Program:
Materials Science and Engineering
Project Description:
Pancreatic cancer is highly aggressive and lethal. Diagnosis often occurs too late, and current treatment methods are largely ineffective. Common research methods for studying pancreatic cancer, including animal models, the use of cell lines, 2D in vitro cell cultures, and 3D in vitro co-cultures poorly replicate the human microenvironment. Broadly, the object of this project was to study pancreatic cancer intravasation (early stages of metastasis) using human-derived tumors embedded in an engineered tissue, surrounding a prefusable microvessel. This system proves to be more replicative of the spatial and temporal dynamics of the native human microenvironment. On a hemacytometer, dispersed perfusate with intravasated tumor cells contained smaller cell clusters on earlier time points and larger cell clusters on later time points. Calculations based on fluorescent images showed a direct correlation between the total number of cells and cell clusters that intravasate and time. There was also a direct correlation between tumor-vessel interactions and the total number of cells and cell clusters that intravasate on a given day.
Team Members
-
[foreach 357]
[if 397 not_equal=””][/if 397][395]
[/foreach 357]
Project Mentors, Sponsors, and Partners
Zhaobin Guo
Peter Chianchiano
Course Faculty
-
[foreach 429]
[if 433 not_equal=””][/if 433][431]
[/foreach 429]
Project Links
Additional Project Information
Project Photo
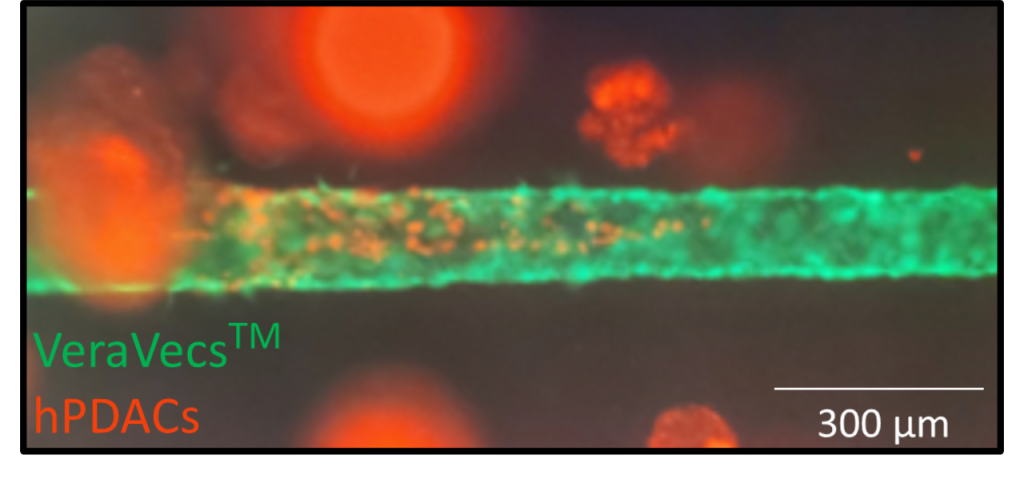
Project Photo Caption:
Endothelial microvessel and cancer tumors revealing intravasation.


